Question: What is decentralized web and what it brings to the table in future?
As the internet evolves, so do the challenges surrounding privacy and security. Traditional web infrastructure, dominated by centralized systems and major corporations, has led to concerns over data privacy, censorship, and control. Enter the decentralized web, or Web 3.0—a revolutionary shift aimed at creating a more open, private, and secure internet. This article explores the concept of the decentralized web, how it operates, its potential benefits, and its implications for the current internet structure.
Understanding the Decentralized Web
The decentralized web, often referred to as Web 3.0, represents a significant departure from the traditional centralized model of the internet. In the traditional web (Web 2.0), data is controlled and stored by a few dominant entities, leading to concerns about data privacy, security breaches, and monopolistic practices.
Core Concepts of the Decentralized Web
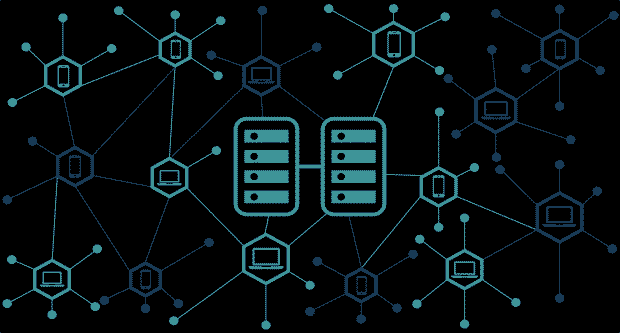
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional web models where data and control are concentrated in central servers, the decentralized web distributes data across a network of computers (nodes). This distribution reduces the risk of single points of failure and enhances the resilience of the network.
- Blockchain Technology: At the heart of many decentralized web applications is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. This technology underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as decentralized applications (dApps).
- Peer-to-Peer Networks: The decentralized web relies on peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, where users can directly share and access data without intermediaries. P2P networks facilitate data exchange, collaboration, and communication in a more direct and decentralized manner.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automatically execute, enforce, or verify contractual agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud.
Benefits of the Decentralized Web
The decentralized web offers numerous advantages over traditional internet models, particularly in terms of privacy, security, and user empowerment.
1. Enhanced Privacy
In a decentralized web, users have greater control over their personal data. Instead of relying on centralized platforms that collect and monetize user data, decentralized applications (dApps) enable users to retain ownership of their data. This shift empowers individuals to decide how and with whom their information is shared, reducing the risk of data breaches and misuse.
2. Improved Security
Decentralization inherently enhances security by eliminating single points of failure. Traditional centralized servers are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches, as compromising a single server can lead to widespread data theft. In contrast, decentralized networks distribute data across multiple nodes, making it more difficult for malicious actors to access or manipulate the entire system.
3. Greater Control and Ownership
The decentralized web empowers users by giving them greater control over their online identities and digital assets. Through blockchain technology and smart contracts, users can manage their digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies and NFTs (non-fungible tokens), with greater transparency and security. This shift reduces reliance on centralized entities and intermediaries.
4. Resistance to Censorship
Centralized platforms are susceptible to censorship and content moderation based on corporate or governmental interests. The decentralized web, by contrast, is designed to be more resistant to censorship. Distributed networks and blockchain technology make it challenging for any single entity to control or suppress content, promoting a more open and inclusive internet.
5. Improved Transparency
Blockchain technology enhances transparency by providing a public, immutable ledger of transactions and activities. This transparency fosters trust and accountability, as users can verify the authenticity of data and transactions. It also enables decentralized applications to operate with greater openness, reducing the potential for fraud and manipulation.
How the Decentralized Web Works
To understand how the decentralized web operates, it’s essential to explore its underlying technologies and protocols.
1. Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) forms the backbone of the decentralized web. Unlike traditional databases, which are centralized and controlled by a single entity, distributed ledgers are maintained across multiple nodes. This technology ensures that every participant has a copy of the ledger, making it more secure and resilient to tampering.
2. Decentralized Storage
Decentralized storage solutions, such as IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), provide a distributed approach to data storage. Instead of storing files on centralized servers, IPFS distributes and replicates data across a network of nodes. This approach enhances data availability, reduces latency, and improves resilience.
3. Cryptographic Security
Cryptographic techniques play a crucial role in securing the decentralized web. Encryption ensures that data is protected from unauthorized access, while digital signatures authenticate transactions and communications. Cryptographic protocols safeguard user privacy and the integrity of data within decentralized networks.
4. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are protocols used to validate and agree on the state of the distributed ledger. Popular consensus mechanisms include proof-of-work (used by Bitcoin) and proof-of-stake (used by Ethereum 2.0). These mechanisms ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
Implications for the Current Internet Structure
The rise of the decentralized web has significant implications for the current internet structure and its stakeholders.
1. Disruption of Traditional Platforms
The decentralized web has the potential to disrupt traditional online platforms and services. Centralized giants, such as social media companies and cloud providers, may face competition from decentralized alternatives that offer greater privacy, security, and user control. This shift could lead to a more diverse and competitive internet landscape.
2. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
The decentralized web presents regulatory and legal challenges, as traditional regulatory frameworks may not fully address the unique characteristics of decentralized systems. Issues related to data protection, intellectual property, and jurisdictional authority may require new approaches and legal considerations.
3. Adoption and Integration
Widespread adoption of the decentralized web will require significant changes in technology, infrastructure, and user behavior. Transitioning from centralized systems to decentralized alternatives involves overcoming technical, logistical, and cultural barriers. However, as the technology matures and gains traction, integration into existing systems and processes may become more feasible.
4. Empowerment of Users
The decentralized web empowers users by giving them greater control over their digital lives. As individuals gain ownership of their data and digital assets, they can participate more actively in shaping the future of the internet. This shift aligns with broader trends towards user-centric and privacy-focused technologies.
Conclusion
The decentralized web represents a transformative shift towards a more private, secure, and user-empowered internet. By leveraging blockchain technology, peer-to-peer networks, and cryptographic security, the decentralized web offers numerous benefits, including enhanced privacy, improved security, and resistance to censorship. As the technology continues to evolve, it has the potential to reshape the internet landscape and create new opportunities for innovation and user empowerment.